Global Positioning System tracking is a method of working out exactly where something is. A GPS tracking system, for example, may be placed in a vehicle, on a cell phone, or on special GPS devices, which can either be a fixed or portable unit. GPS works by providing information on exact location. It can also track the movement of a vehicle or person. So, for example, a GPS tracking system can be used by a company to monitor the route and progress of a delivery truck, and by parents to check on the location of their child, or even to monitor high-valued assets in transit.

A GPS tracking system uses the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) network. This network incorporates a range of satellites that use microwave signals that are transmitted to GPS devices to give information on location, vehicle speed, time and direction. So, a GPS tracking system can potentially give both real-time and historic navigation data on any kind of journey.
GPS provides special satellite signals, which are processed by a receiver. These GPS receivers not only track the exact location but can also compute velocity and time. The positions can even be computed in three-dimensional views with the help of four GPS satellite signals. The Space Segment of the Global Positioning System consists of 27 Earth-orbiting GPS satellites. There are 24 operational and 3 extra (in case one fails) satellites that move round the Earth each 12 hours and send radio signals from space that are received by the GPS receiver.
The control of the Positioning System consists of different tracking stations that are located across the globe. These monitoring stations help in tracking signals from the GPS satellites that are continuously orbiting the earth. Space vehicles transmit microwave carrier signals. The users of Global Positioning Systems have GPS receivers that convert these satellite signals so that one can estimate the actual position, velocity and time.
The operation of the system is based on a simple mathematical principle called trilateration. Trilateration falls into two categories: 2-D Trilateration and 3-D Trilateration. In order to make the simple mathematical calculation the GPS receiver must know two things. First it must know the location of the place is to be traced by at least three satellites above the place. Second, it must know the distance between the place and each of those Space Vehicles. Units that have multiple receivers that pick up signals from several GPS satellites at a same time. These radio waves are electromagnetic energy that travels at the speed of light.
A GPS tracking system can work in various ways. From a commercial perspective, GPS devices are generally used to record the position of vehicles as they make their journeys. Some systems will store the data within the GPS tracking system itself (known as passive tracking) and some send the information to a centralized database or system via a modem within the GPS system unit on a regular basis (known as active tracking) or 2-Way GPS.
A passive GPS tracking system will monitor location and will store its data on journeys based on certain types of events. So, for example, this kind of GPS system may log data such as where the device has traveled in the past 12 hours. The data stored on this kind of GPS tracking system is usually stored in internal memory or on a memory card, which can then be downloaded to a computer at a later date for analysis. In some cases the data can be sent automatically for wireless download at predetermined points/times or can be requested at specific points during the journey.
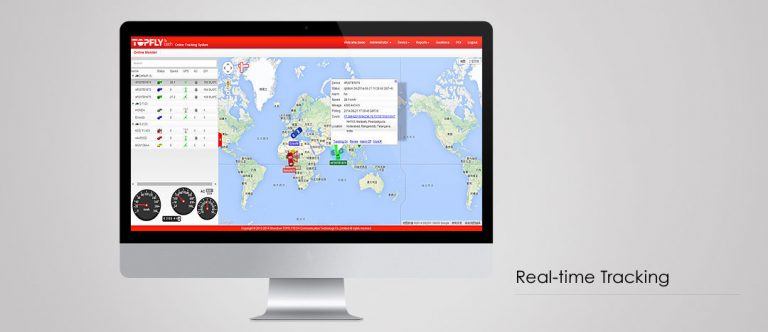
An active GPS tracking system is also known as a real-time system as this method automatically sends the information on the GPS system to a central tracking portal or system in real-time as it happens. This kind of system is usually a better option for commercial purposes such as fleet tracking or monitoring of people, such as children or elderly, as it allows a caregiver to know exactly where loved ones are, whether they are on time and whether they are where they are supposed to be during a journey. This is also a useful way of monitoring the behavior of employees as they carry out their work and of streamlining internal processes and procedures for delivery fleets.
Real-time tracking is also particularly useful from a security perspective as it allows vehicle owners to pinpoint the exact location of a vehicle at any given time. And, the GPS tracking system in the vehicle may then be able to help police work out where the vehicle was taken to if it was stolen.
Mobile Phone Tracking
The development of communications technology has long since surpassed the sole ability to access others when they are mobile. Today, mobile communication devices are becoming much more advanced and offer more than the ability to just carry on a conversation. Cell phone GPS tracking is one of those advances.
All cell phones constantly broadcast a radio signal, even when not on a call. The cell phone companies have been able to estimate the location of a cell phone for many years using triangulation information from the towers receiving the signal. However, the introduction of GPS technology into cell phones has meant that cell phone GPS tracking now makes this information a lot more accurate.
With GPS technology now more commonplace in many new smartphones, this means that the location of anyone carrying a GPS enabled smartphone can be accurately tracked at any time. Cell phone GPS tracking can therefore be a useful feature for business owners, parents, friends and co-workers looking to connect with one another. GPS Tracking Apps provides a suit of Apps for the iPhone, iPad, Android, Blackberry and latest Samsung operating system bada all of which can be used to track one another on a location-based social networking portal or from phone to phone.
The technology of locating is based on measuring power levels and antenna patterns and uses the concept that a mobile phone always communicates wirelessly with one of the closest base stations, so if you know which base station the phone communicates with, you know that the phone is close to the respective base station.
Advanced systems determine the sector in which the mobile phone resides and roughly estimate also the distance to the base station. Further approximation can be accomplished by interpolating signals between adjacent antenna towers. Qualified services may achieve a precision of down to 50 meters in urban areas where mobile traffic and density of antenna towers (base stations) is sufficiently high. Rural and desolate areas may see miles between base stations and therefore determine locations less precisely.
GSM localization is the use of multilateration to determine the location of GSM mobile phones, usually with the intent to locate the user.
Localization-based Systems can be broadly divided into: 1). Network based; 2). Handset based; 3). Hybrid.
Network Based
Network-based techniques utilize the service provider’s network infrastructure to identify the location of the handset. The advantage of network-based techniques (from mobile operator’s point of view) is that they can be implemented non-intrusively, without affecting the handsets.
The accuracy of network-based techniques varies, with cell identification as the least accurate and triangulation as the most accurate. The accuracy of network-based techniques is closely dependent on the concentration of base station cells, with urban environments achieving the highest possible accuracy.
Handset Based
Handset-based technology requires the installation of client software on the handset to determine its location for E-911 purposes. This technique determines the location of the handset by computing its location by cell identification, signal strengths of the home and neighboring cells, which is continuously sent to the carrier. In addition, if the handset is also equipped with GPS then significantly more precise location information is then sent from the handset to the carrier.
This technology requires the installation of client software on the mobile phone, which acts as its biggest drawback, since it’s difficult to install a software on a mobile phone without the user’s consent. More importantly, the software has to be compatible with various operating systems. It requires the active cooperation of the mobile subscriber as well as software that must be able to handle the different operating systems of the handsets. Typically, smartphones, such as one based on Symbain, Windows Mobile, iPhone/iPhoneOS or Android would be able to run such software.
Hybrid
Hybrid oositioning systems use a combination of network-based and handset-based technologies for location determination. One example would be Assisted GPS, which uses both GPS and network information to compute the location. Hybrid-based techniques give the best accuracy of the three but inherit the limitations and challenges of network-based and handset-based technologies.
Examples of LBS (Location-Based Service) technologies include:
1. Cell Identification – The accuracy of this method can be as good as a few hundred meters in urban areas, but as poor as 35 km in suburban areas and rural zones. The accuracy depends on the known range of the particular network base station serving the handset at the time of positioning.
2. Enhanced Cell Identification – With this method, one can get a precision similar to Cell Identification, but for rural areas, with circular sectors of 550 meters.
3. U-TDOA -Uplink- Time difference of arrival – The network determines the time difference and therefore the distance from each base station to the mobile phone.
4. TOA -Time of arrival – This technology uses the absolute time of arrival at a certain base station rather than the difference between two stations.
5. AOA -Angle of Arrival – AOA mechanism locates the mobile phone at the point where the lines along the angles from each base station intersect.
6. E-OTD -Enhanced Observed Time Difference is similar to U-TDOA, but the location is estimated using measurements made by the mobile phone, rather than by base station.
7. Assisted GPS- A largely GPS-based technology, which uses an operator-maintained ground station to correct for GPS errors caused by the atmosphere/topography. Assisted-GPS positioning technology typically falls back to cell-based positioning methods when indoors or in an urban canyon environment.
8. Hybrid – As mentioned above, hybrid-positioning systems use different methods depending on which signals are locally available.
Importance of GPS systems
GPS is important as it helps you to figure out where you are and where you are going when you are traveling from one place to another. Navigation and positioning are important but cumbersome activities, which GPS makes it easier. Once GPS locates your position, and then it starts tracing other factors like speed, bearing, tracks, trip distance, sunrise/sunset time, distance to destination and several other details. GPS uses ‘man-made’ stars as reference points to calculate positions accurate to a matter of meters. However, with recent forms of GPS you can make measurements much better than centimeter readings. So it is with the aid of GPS that you can give a unique and specified address to every square meter on the planet. So these days GPS finds its way into cars, planes, boats, construction equipments, smartphones, laptop computers and shoes (www.gpsshoe.com) and belts. In addition, GPS tracking system installed in the phone can greatly help an individual to get automated GPS information through their cell phones.
– Extracted from www.eetimes.com